
Other mirrors types for "grazing schemes"- see
here , for example
ellipsoidal mirrors or
off axis parabolic mirrors .
A toroidal mirror is part of the surface of a toroid (torus, “donut”). In the figure below this part of the surface
painted red. The toroid itself is painted yellow.
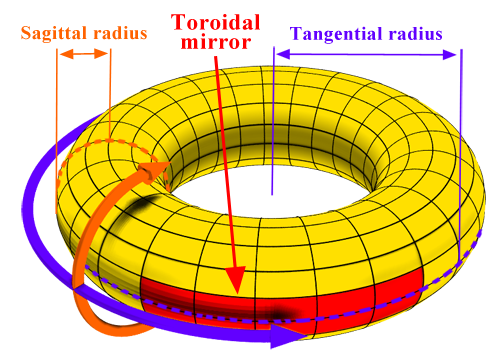
To define a toroidal surface,
it is enough to indicate its two radii:
tangential Rt (purple)
and sagittal Rs (orange).
A toroidal mirror is usually used when it is necessary to focus divergent radiation from a point source to a point
and at the same time the angle of incidence is far from normal. (see picture below). Sometimes these mirrors are at the same angles
incidences are used to create a collimated beam (or vice versa, focus a collimated beam).
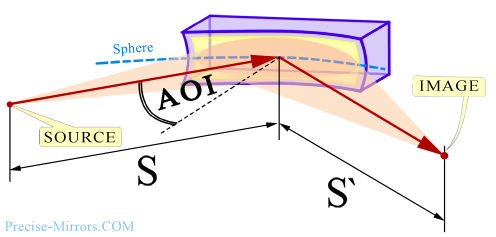
If (as is usually the case) Rs/Rt=Cos2(AOI),
then the following formulas are true for toroidal mirrors:
![]()
where S, S' and AOI - see the figure above,
Rt and Rs - see the figure to the left.
Toroidal mirrors are often used to reflect radiation with short wavelengths (less than 50-100 nm and up to units of nm). In order to achieve a noticeable reflectance of the mirror in this spectral range, it is necessary to use very large angles of incidence (usually 70-85 degrees and up to 89.5 degrees, hence the term "grazing angle", which is equal to 90 degrees minus the angle of incidence). Spherical surfaces at such large angles of incidence will give very large aberrations, so instead they use a toroidal shape of the reflective surface, which is almost free of this drawback.
| Mirror minimal and maximal sizes: | from 40 mm to 1200 mm | |
| Mirror substrate material: | Astrositall, by request: Zerodur, UV FS, Si and other. | |
| Coatings: | Metallic (Ag, Au, Al) and special EUV|XUV. | |
| Manufacture accuracy (RMS, λ=633 nm) | Base | Maximal |
| surface shapes, spherical mirrors | up to λ/140 | up to λ/400 |
| surface shapes, aspherical mirrors | up to λ/100 | up to λ/300 |
| Radiuses manufacture accuracy | up to ±0.05% | up to ±0.001% |
| Surface microroughness, RMS | 0.3 nm | 0.15 нм |
| Cosmetic quality (per square inch) | 40/20 scratch/dig | 10/5 scratch/dig |
The main advantage of toroidal mirrors is the relative simplicity of their production and, as a result, their smaller cost and shorter production time. Also, almost every production facility can produce toroidal mirrors (another issue is that to work in deep ultraviolet light, very high precision manufacturing of the reflective surface and small micro-roughness - for example RMS λ/90 and 0.2 nm, respectively - but to do this kind of work very few people can, since almost everywhere in the world the maximum possibilities are about RMS λ/20 and 0.5 nm).
The main disadvantage of toroidal mirrors is the presence of spherical aberrations, which can greatly degrade the quality (shape, uniformity energy distribution) and increase the size of the focused radiation (up to millimeter focused spot sizes, compare it with standard values of tens of microns for "good mirrors"). Please note that these distortions will be present even with the highest precision in manufacturing the shape of the reflective surface. It is important to understand that the use of optical schemes with the so-called “2f geometry” (this is when S=S', see figure above) not provides a guaranteed solution to the problem of spherical aberrations, you can see it in the example here . There is also a widespread misconception that using two identical conjugated toroidal mirrors eliminates large spherical distortions. (in theory this is true - the second toroid must compensate for the distortions introduced by the first toroid). But in real practice everything is much more complicated, for example, see the third page of our standard quotation , where the stability of a real scheme with two identical conjugate toroidal mirrors is simulated).
Typically, it is very important for the customer how small a spot in the image plane can be formed by the mirror (see figure below). Even if used scheme where S' is equal to infinity (collimated beam after reflection), this parameter allows You to estimate how good the output beam will be.
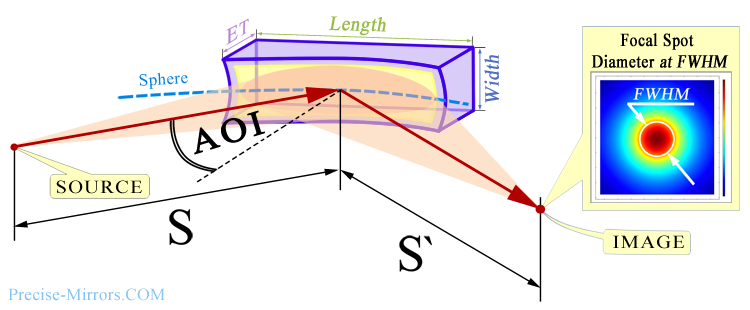
The size of the spot in the image plane can be influenced by many different factors, but from actual practice these are mainly spherical aberrations, manufacturing precision of the mirror surface shape, and sometimes diffraction limitations at the operating wavelength. Also, the accuracy of the adjustment is often extremely important, since sometimes for example, an error in mirror position of just a few microns can increase the diameter of the focused spot several times.
The general principle is that the closer the size of focused spot
to the diffraction limit, the more expensive such a mirror is.
It depends on Your task and the funds allocated for the purchase. The most competent and correct way would be to fill out our special "request form" (here it is help in filling out (pdf) ). It is also advisable to attach to the request form a description of Your optical design (at least in words), in which the mirror will operate and all this send to our email quote@precise-mirrors.ru. Next, our specialists will select several suitable options for You (see example of a typical quote for single mirror or for two conjugated mirrors ).
You can also send a detailed exact specification of the mirror You need with drawings, a description of the type of surface shape, calculated radii, with all tolerances, etc. But even in this case, it is better to add at least minimal information on the angle of incidence, the size of the source and the desired image size. From our extensive practice, in such cases it is often possible to at least optimize the radius, with which the result will be slightly better and the customer does not incur any additional costs.
You also don’t have to fill out "request form" , and do not send a detailed exact specification of the mirror you need, but instead send a description of Your task (mirror) in any form to the same email address quote@precise-mirrors.ru. But in this case, such a request may take much longer to process.